The use of preprints has increased rapidly over the last few years, especially in biomedical and life sciences. We’ve been tracking changes in the preprint landscape over time and maintain a page dedicated to this topic. Here are some of the most notable trends over the last year.
Adoption and sources
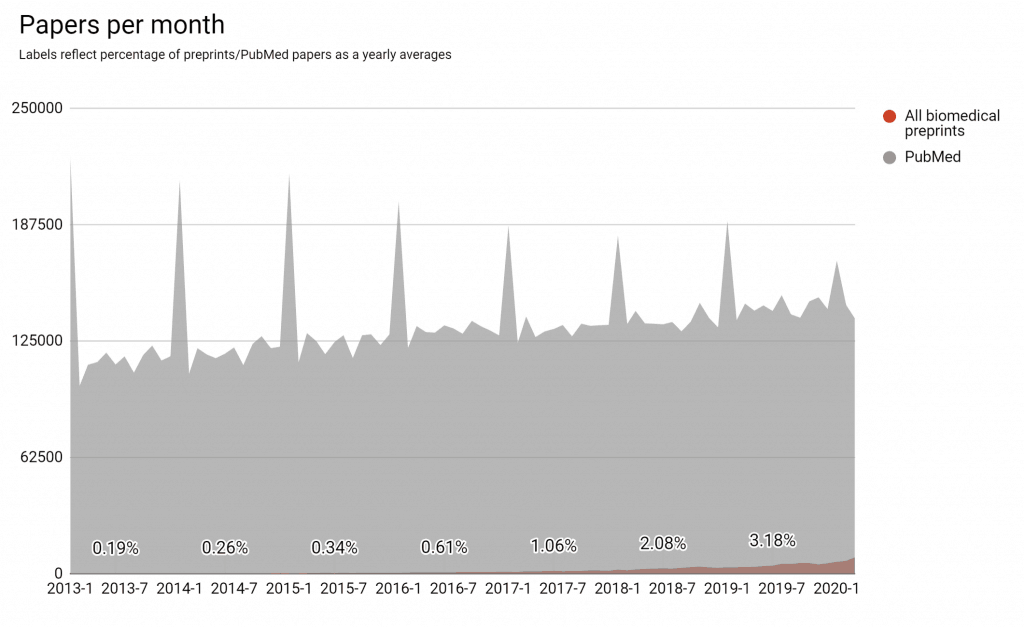
The rate of life sciences preprints posted per month continues to increase, putting our current estimate of the fraction of the biomedical literature represented as preprints at just over 3% (data). In the last year, the source of these preprints has undergone a notable shift driven by the emergence of In Review, Springer Nature’s preprint service on the Research Square platform, as well as continued growth of bioRxiv. MedRxiv also launched in the last year, and submissions are growing steadily, while PeerJ Preprints closed.
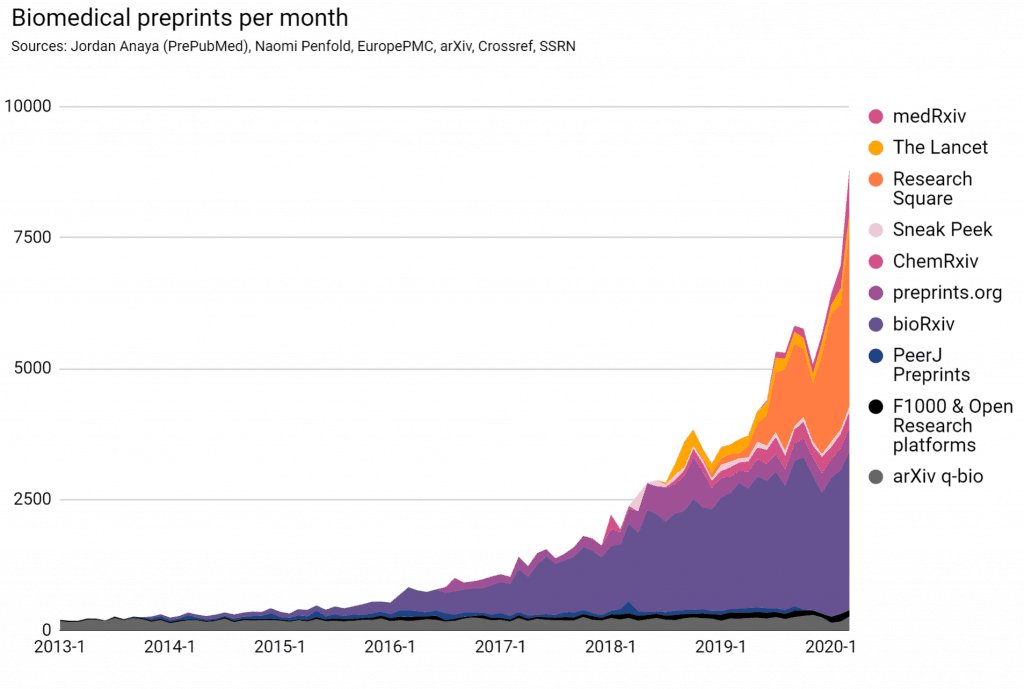
Note that this chart does not yet incorporate preprints from OSF.
COVID-19 response
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, over 100 publishers, funders, and other organizations announced support for preprints, and many servers offer collections that highlight relevant work:
Other support
At the same time, technological support for community-driven preprint servers is in flux. COS has implemented a sustainability model for OSF preprints, forcing some of the community servers to leave the platform. Meanwhile, PKP has released a beta of Open Preprint Systems, an open source platform that can be set up to run on any server.
Meanwhile, several new funder policies have further encouraged preprint growth. Wellcome’s new OA policy requires preprinting for work of significant benefit to human health, and two Parkinson’s funders, ASAP and MJFF, both announced preprint requirements.
Infrastructure continued to evolve to support preprinting, with enhancements at ORCID and Europe PMC.
Review projects targeting preprints have also expanded. In late 2019, bioRxiv launched TRiP, a collaboration with Hypothesis that will overlay peer review on preprints. An ASAPbio-EMBO collaboration funded by The Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust, Review Commons, is one such project. With funding from CZI, we are tracking other projects at ReimagineReview. One of these, PREreview, was started by ASAPbio ambassadors and is now building a platform for rapid review of outbreak science.
Data
Cite as: Polka, Jessica K., & Penfold, Naomi C. (2020). Biomedical preprints per month, by source and as a fraction of total literature (Version 2.0) [Data set]. Zenodo. http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3739414








1 Comment